AlaskaUSA: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Last Frontier unveils the captivating story of Alaska, a land of unparalleled beauty, rich history, and abundant resources. From its breathtaking landscapes to its diverse wildlife, AlaskaUSA delves into the heart of this extraordinary state, offering readers a comprehensive understanding of its geography, climate, culture, and more.
Embark on an enthralling journey through Alaska’s vast wilderness, discover the challenges and opportunities it faces, and gain insights into the unique experiences that await those who dare to explore its untamed frontiers.
Alaska’s Geography
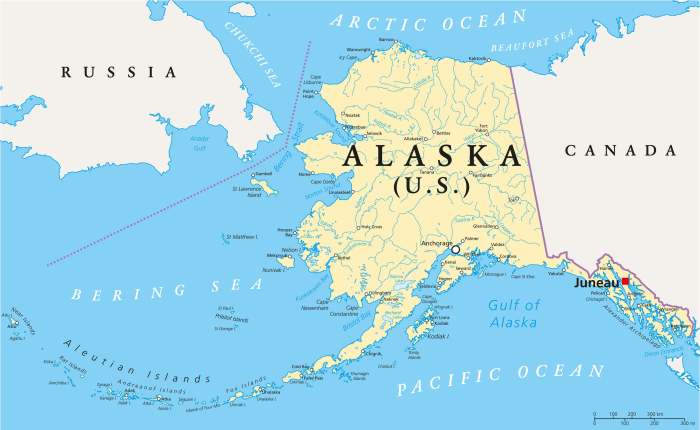
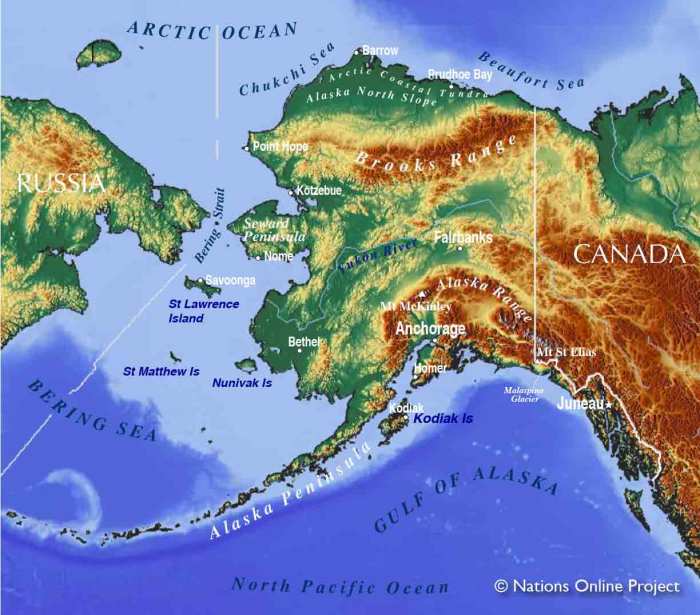
Alaska, the largest state in the United States, boasts a unique location and a vast, diverse landscape. Situated in the northwest corner of North America, it shares borders with Canada to the east and Russia to the west, and its coastline stretches along the Arctic Ocean to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south.
Alaska’s Size and Diversity
Alaska’s sheer size is remarkable, spanning over 665,000 square miles. This vast expanse encompasses a wide range of landscapes, from towering mountains and glaciers to vast forests, tundra, and coastal plains. The state’s geography is shaped by its geological history, which includes volcanic activity, glaciation, and tectonic plate movement.
Major Mountain Ranges
Alaska is home to some of the most impressive mountain ranges in the world. The Alaska Range, located in the south-central part of the state, is home to Mount Denali, the highest peak in North America at 20,310 feet. Other notable ranges include the Brooks Range in the north, the Wrangell Mountains in the southeast, and the Aleutian Range in the southwest.
Rivers and Glaciers
Alaska’s abundant water resources are a testament to its pristine natural environment. The Yukon River, the longest river in Alaska, flows for over 1,900 miles from Canada through central Alaska and empties into the Bering Sea. Other major rivers include the Kuskokwim, Tanana, and Copper rivers. Alaska is also home to numerous glaciers, including the massive Malaspina Glacier, which covers an area of over 1,500 square miles.
Alaska’s Climate
Alaska’s climate is a diverse and ever-changing tapestry, shaped by a complex interplay of factors. Its vast size, unique geography, and proximity to the Arctic and Pacific Oceans all contribute to its varied and dynamic weather patterns.
Factors Influencing Alaska’s Climate
- Latitude and proximity to the Arctic Circle: Alaska’s high latitude and proximity to the Arctic Circle result in extreme seasonal variations in daylight and temperature.
- Mountain ranges: The Alaska Range and the Brooks Range act as barriers to moisture-carrying winds, creating distinct climate zones within the state.
- Coastal influences: The Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Alaska exert a moderating influence on coastal climates, resulting in milder temperatures and increased precipitation.
- Ocean currents: The warm Alaska Current and the cold Bering Sea Current influence Alaska’s coastal temperatures and precipitation patterns.
Differences Between Coastal and Interior Climates
Alaska’s coastal regions experience a maritime climate, characterized by milder temperatures, higher precipitation, and frequent fog. The interior, on the other hand, has a continental climate with extreme temperature variations, low precipitation, and clear skies.
Unique Weather Patterns and Seasonal Variations
Alaska’s weather patterns are highly variable, with frequent storms, blizzards, and extreme cold. The state experiences long, cold winters and short, mild summers. During the winter months, temperatures can drop below -60°F (-51°C) in the interior, while coastal areas typically stay above freezing.
Alaska’s History
Alaska’s history is a tapestry woven with the threads of indigenous cultures, exploration, fur trade, and gold mining. From its ancient roots to its present-day status as the largest state in the United States, Alaska’s past has shaped its unique identity.
Indigenous Roots
Alaska’s indigenous population, composed of various Native American tribes, has inhabited the land for thousands of years. These tribes, including the Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, Athabaskan, and Yup’ik, developed distinct cultures and traditions adapted to the region’s diverse ecosystems.
If you’re looking for a once-in-a-lifetime experience, consider an expedition to Alaska’s remote wilderness. Explore breathtaking glaciers, encounter majestic wildlife, and immerse yourself in the rich culture of the Last Frontier. And while you’re planning your Alaskan adventure, don’t forget to delve into the captivating cultural tours in Europe.
From exploring ancient ruins to indulging in culinary delights, there’s something for every traveler seeking cultural enrichment. But don’t let your European adventure overshadow the wonders of Alaska, a land where rugged beauty and cultural heritage intertwine seamlessly.
Exploration and Fur Trade
In the 18th century, Russian explorers ventured into Alaska, establishing trading posts and exploiting the region’s abundant fur resources. The fur trade became a major economic driver, leading to conflicts between indigenous tribes and Russian fur traders.
Gold Mining and American Acquisition
In the late 19th century, the discovery of gold in Alaska sparked a massive influx of prospectors and settlers. The Klondike Gold Rush of 1896 brought thousands of people to the region, transforming Alaska’s economy and leading to its annexation by the United States in 1867.
Challenges and Opportunities for Native Americans
Alaska’s history has presented both challenges and opportunities for its Native American population. While the influx of settlers and development brought economic opportunities, it also led to cultural displacement and loss of traditional lands.
In recent decades, Alaska’s Native Americans have made significant strides in asserting their rights and preserving their cultures. The Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971 recognized the land rights of indigenous tribes and provided for the establishment of Native corporations.
Alaska’s stunning landscapes and abundant wildlife make it a dream destination for families. However, it’s not always easy to find affordable options. Check out budget family vacations for tips on how to save money on your next Alaskan adventure. From camping and RV rentals to discounts on attractions, there are plenty of ways to experience the Last Frontier without breaking the bank.
Alaska offers unforgettable memories for families of all ages.
Today, Alaska’s Native American population continues to play a vital role in the state’s cultural, economic, and political landscape, contributing to its unique heritage and identity.
Alaska’s Culture
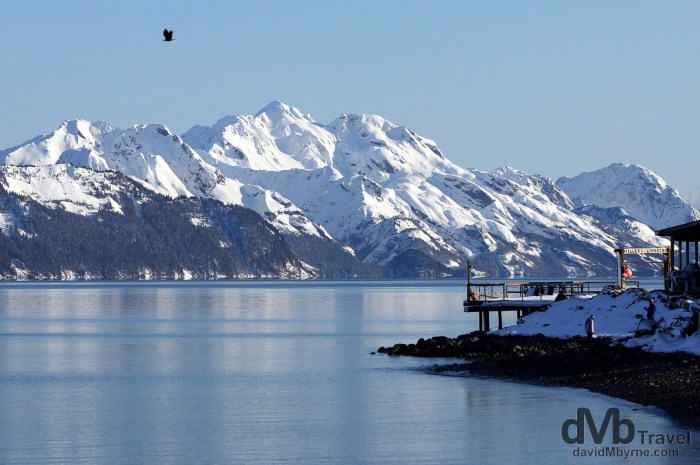

Alaska is a melting pot of diverse cultures, influenced by its indigenous peoples, Russian and American settlers, and other immigrant communities. The state’s rich cultural heritage is reflected in its unique traditions, arts, and crafts.
Indigenous Cultures
Alaska is home to 11 major indigenous cultures, each with its distinct language, traditions, and art forms. These cultures have thrived for thousands of years, adapting to the state’s harsh environment and abundant natural resources.
- Athabaskan: The Athabaskan people inhabit the interior of Alaska and speak various Athabaskan languages. They are known for their beadwork, basketry, and storytelling traditions.
- Tlingit: The Tlingit people reside in southeastern Alaska and are renowned for their intricate carvings, totem poles, and traditional regalia.
- Haida: The Haida people live in the southernmost part of Alaska and are famous for their distinctive argillite carvings, basketry, and jewelry.
Russian and American Influences
Alaska’s history as a Russian colony and later as an American territory has significantly influenced its culture. Russian Orthodox churches, log cabins, and other architectural styles can still be found throughout the state. American influences are evident in the state’s legal system, education system, and popular culture.
Unique Traditions and Arts
Alaska’s Native American communities have preserved many unique traditions and art forms that reflect their close connection to the land and its resources. These include:
- Subsistence Hunting and Fishing: Subsistence hunting and fishing are essential to the way of life for many indigenous Alaskans, providing food, clothing, and other resources.
- Potlatch Ceremonies: Potlatch ceremonies are traditional gatherings where indigenous communities share food, gifts, and stories, strengthening social bonds and passing on cultural knowledge.
- Totem Poles: Totem poles are carved wooden structures that serve as symbols of family history, clan identity, and cultural beliefs.
Alaska’s Wildlife
Alaska’s vast and pristine wilderness is home to an abundance and diversity of wildlife. From majestic whales and soaring eagles to elusive wolves and playful otters, Alaska’s wildlife plays a crucial role in the state’s ecosystem and economy.
The state’s varied habitats, including forests, mountains, tundra, and coastline, provide diverse ecosystems that support a wide range of species. Alaska’s wildlife is not only a source of awe and wonder for visitors but also a vital part of the local culture and traditions.
Importance to Ecosystem
Alaska’s wildlife is integral to the state’s ecosystem. Predators like wolves and bears help control populations of herbivores, maintaining a balance in the food chain. Scavengers, such as ravens and eagles, play a crucial role in removing carcasses, preventing the spread of disease.
Wildlife also contributes to the health of forests and tundra. Beavers build dams, creating wetlands that support diverse plant and animal life. Salmon, a keystone species, provide nutrients to both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems during their spawning runs.
Importance to Economy
Wildlife tourism is a significant contributor to Alaska’s economy. Visitors from around the world come to experience the state’s abundant wildlife, supporting local businesses and communities.
Commercial fishing and hunting are also important industries in Alaska. Salmon, halibut, and crab are harvested from the state’s waters, while moose, caribou, and bear hunting provide sustenance and income for local communities.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Alaska’s wildlife is abundant, it faces several challenges. Climate change, habitat loss, and human encroachment are all threats to the state’s wildlife populations.
However, there are also opportunities for wildlife conservation in Alaska. The state has vast protected areas, including national parks and wildlife refuges, that provide safe havens for animals.
Education and outreach programs are also essential for fostering a culture of wildlife appreciation and stewardship. By working together, Alaskans and visitors alike can ensure the long-term health and well-being of the state’s wildlife.
Alaska’s Natural Resources
Alaska is blessed with a vast abundance of natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and timber. These resources have played a significant role in shaping the state’s economy and environment.
Oil and Gas
Alaska is the largest oil-producing state in the United States. The Prudhoe Bay oil field, discovered in 1968, has been a major source of revenue for the state. Oil production has provided jobs and supported economic growth in Alaska, but it has also raised concerns about environmental impacts, such as oil spills and air pollution.
Minerals
Alaska is also rich in minerals, including gold, silver, copper, and zinc. Mining has been a significant industry in the state since the late 19th century. However, mining can also have negative environmental impacts, such as water pollution and habitat destruction.
Timber
Alaska has vast forests, which provide timber for the state’s lumber industry. Timber harvesting can provide jobs and support economic growth, but it can also lead to deforestation and habitat loss.
Economic and Environmental Implications
Alaska’s natural resource industries have significant economic and environmental implications. These industries provide jobs and support economic growth, but they can also have negative environmental impacts. It is important to find ways to sustainably manage Alaska’s natural resources to protect the environment while still benefiting from the economic benefits they provide.
Challenges and Opportunities
There are several challenges and opportunities related to sustainable resource management in Alaska. One challenge is to find ways to reduce the environmental impacts of resource extraction. Another challenge is to ensure that the benefits of resource development are shared equitably among all Alaskans. There are also opportunities to develop new technologies and practices that can help to minimize the environmental impacts of resource extraction. Additionally, there are opportunities to create new jobs and economic opportunities in the renewable energy sector.
Alaska’s Tourism Industry: Alaskausa
Tourism plays a vital role in Alaska’s economy, contributing significantly to job creation, tax revenue, and infrastructure development. The state’s vast and diverse landscapes, rich wildlife, and unique cultural experiences attract visitors from around the world.
Types of Tourism Activities
Alaska offers a wide range of tourism activities to suit every interest and preference, including:
- Wildlife Viewing: Visitors can witness an abundance of wildlife, including bears, whales, moose, and eagles, in their natural habitats.
- Adventure Sports: Alaska is a paradise for adventure seekers, offering opportunities for hiking, kayaking, rafting, fishing, and snowmobiling.
- Cultural Experiences: Tourists can immerse themselves in the unique cultures of Alaska’s Native American and Russian heritage through visits to museums, historical sites, and cultural events.
Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Tourism Development
While tourism brings economic benefits, it also presents challenges related to sustainability. Managing the impacts of tourism on Alaska’s fragile ecosystems and cultural heritage is crucial. Key considerations include:
- Environmental Conservation: Minimizing the impact of tourism on wildlife, landscapes, and air and water quality.
- Cultural Preservation: Respecting and preserving the cultural traditions and values of Alaska’s Native American and Russian communities.
- Economic Diversification: Developing tourism as a sustainable economic driver while promoting other industries.
Alaska’s Infrastructure and Transportation
Alaska’s vast size, rugged terrain, and extreme climate present significant challenges to infrastructure development and transportation. However, these challenges also create unique opportunities for innovation and sustainable solutions.
Transportation plays a vital role in connecting Alaska’s remote communities and supporting its economy. The state’s transportation network includes a mix of highways, railroads, airports, and waterways.
Challenges and Opportunities in Infrastructure Development
Developing and maintaining infrastructure in Alaska is costly and complex due to the state’s vast size, harsh climate, and rugged terrain. Permafrost, which underlies much of Alaska, poses challenges for construction and maintenance, as it can thaw and destabilize structures.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation. For example, engineers have developed specialized construction techniques to mitigate the effects of permafrost and extreme cold.
Transportation in Remote Communities, Alaskausa
Transportation is essential for connecting Alaska’s remote communities to the rest of the state and the world. The Alaska Marine Highway System provides ferry service to coastal communities, while the Alaska Railroad connects interior communities to Anchorage and Fairbanks.
Air travel is also crucial for remote communities, as it is often the only way to access essential services and goods. Small aircraft, including bush planes, play a vital role in providing transportation to remote areas.
Unique Transportation Challenges
Alaska’s vast size and harsh climate pose unique transportation challenges. The state’s long distances and rugged terrain make it difficult and expensive to build and maintain roads and railroads.
Extreme cold and snow can also disrupt transportation, especially during the winter months. Ice roads, which are built on frozen rivers and lakes, provide a temporary solution during the winter, but they can be dangerous and are not suitable for heavy traffic.
Alaska’s Education System

Alaska’s education system is a complex and dynamic one, with a rich history and a bright future. The state’s vast size and diverse population present unique challenges and opportunities for educators, and the system is constantly evolving to meet the needs of its students.
One of the strengths of Alaska’s education system is its commitment to equity. The state constitution guarantees every child the right to a quality education, regardless of their race, gender, or socioeconomic status. This commitment is reflected in the state’s funding formula, which allocates more resources to schools with high concentrations of students from low-income families.
AlaskaUSA is renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty, but it also offers luxurious travel experiences. For those seeking exclusive adventures, consider exploring luxury travel deals that cater to discerning travelers. From private glacier tours to helicopter excursions over towering mountains, AlaskaUSA offers a range of options to indulge in the ultimate travel experience.
Another strength of Alaska’s education system is its focus on innovation. The state has been a leader in the development of new educational programs and technologies, such as online learning and personalized learning plans. These programs are designed to meet the needs of Alaska’s diverse student population and to prepare students for success in the 21st-century workforce.
Challenges
Despite its strengths, Alaska’s education system faces a number of challenges. One of the biggest challenges is the state’s vast size. Alaska is the largest state in the United States, and its schools are spread out over a vast area. This makes it difficult to provide equitable access to quality education for all students.
Another challenge facing Alaska’s education system is the state’s high poverty rate. Alaska has one of the highest poverty rates in the United States, and this poverty can have a negative impact on students’ academic achievement. Students who live in poverty are more likely to experience food insecurity, housing instability, and other challenges that can make it difficult to focus on school.
Opportunities
Despite the challenges it faces, Alaska’s education system has a number of opportunities for improvement. One of the biggest opportunities is the state’s strong economy. Alaska has a healthy economy, and this provides the state with the resources to invest in education. The state has also made a commitment to increasing funding for education, and this will help to improve the quality of education for all students.
Another opportunity for Alaska’s education system is the state’s commitment to innovation. The state has been a leader in the development of new educational programs and technologies, and this commitment is continuing. The state is also working to develop new partnerships with businesses and community organizations to provide students with more opportunities to learn and grow.
The Role of Education in Shaping Alaska’s Future
Education plays a vital role in shaping Alaska’s future. A well-educated workforce is essential for the state’s economic development, and a strong education system will help to ensure that all Alaskans have the opportunity to succeed.
The state of Alaska is committed to providing all students with a quality education. The state is working to address the challenges facing its education system, and it is investing in new programs and technologies to improve the quality of education for all students.
Alaska’s Healthcare System
Alaska’s healthcare system is a complex and dynamic network of providers, facilities, and programs that serve the unique needs of a vast and remote state. Despite significant challenges, Alaska’s healthcare system has made strides in improving access to care and health outcomes for its residents.
The vast and remote nature of Alaska poses significant challenges to providing healthcare services. The state’s size, rugged terrain, and dispersed population make it difficult to deliver care to rural communities and isolated areas. In addition, Alaska’s extreme climate conditions can further complicate the delivery of healthcare services, particularly during winter months.
Challenges
One of the primary challenges facing Alaska’s healthcare system is the shortage of healthcare professionals. The state has a lower density of healthcare providers compared to other states, and many rural communities lack access to basic medical services. This shortage is particularly acute in specialized fields such as mental health and addiction treatment.
Another challenge is the high cost of healthcare in Alaska. The state’s remote location and limited competition among healthcare providers contribute to higher costs for patients. In addition, the state’s high poverty rate and lack of affordable housing can make it difficult for low-income Alaskans to access healthcare services.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, Alaska’s healthcare system has made significant progress in recent years. The state has invested in telemedicine and telehealth technologies to improve access to care in rural areas. In addition, Alaska has implemented a number of innovative programs to address the unique healthcare needs of its residents, such as the Alaska Tribal Health System and the Alaska Native Medical Center.
Final Conclusion
AlaskaUSA concludes by highlighting the delicate balance between preserving Alaska’s pristine environment and harnessing its economic potential. It underscores the need for responsible resource management, sustainable tourism practices, and a commitment to improving the lives of all Alaskans.
As the final chapter closes, AlaskaUSA leaves readers with a profound appreciation for the Last Frontier, its rugged beauty, and the indomitable spirit of its people.
Q&A
What is the largest city in Alaska?
Anchorage
What is the highest mountain in Alaska?
Denali (Mount McKinley)
What is the largest national park in Alaska?
Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve